Customer Experience (CX) as a differentiator
Why Customer Experience is so important!

Customer experience (CX) describes how customers perceive a brand or a company.
It is about the overall experience: The customer experience includes all the experiences that customers have with it at the various online or offline touchpoints. It begins with the initial perception of the brand and is subsequently shaped by each subsequent contact.
Today, there are numerous ways for real and potential customers to interact with a brand. These include visits to a retail store, recommendations from acquaintances, and marketing campaigns, as well as the supplier’s website, social media, or mobile apps.
The experiences customers have in the process are crucial for their behavior. They have a direct influence on their buying behavior, but also on the evaluation of a brand in communication with others. A positive customer experience is a key factor for competitiveness and sustainable economic success. Companies can shape this experience in a targeted manner – but to do so, they need to know their customers’ expectations.

What is Customer Experience?
The customer experience encompasses all aspects of a brand that influence the customer experience. A successful brand must be positively experienced by potential customers at all points of contact during the customer journey.
In addition to the respective concrete interactions, emotional components also play a role here. The perception of the brand in the context of the various contacts ultimately forms an overall experience. If it is positive, this results in a sustainable customer relationship and customer loyalty, as the brand becomes indispensable for the customer.
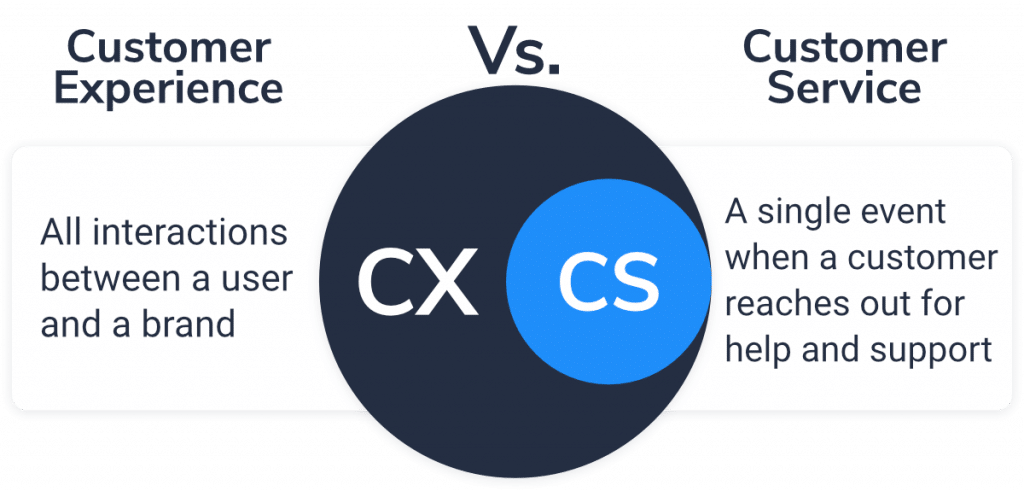
Customer Experience (CX) vs. Customer Service (CS)
Customer experience and customer service are not identical. Customer service, in direct or digitally mediated form, is a component of CX – but there are many other components that go into the customer experience.
Dave Dyson of Zendesk describes CX as the sum of all interactions between customers and brands or companies. The overall experience is shaped by all stages and aspects of the customer journey:
- The initial contact with a brand, for example through marketing campaigns.
- The buying experience
- The quality of the product offered
- The quality of customer service after the purchase
- and much more.
CX focuses on the totality of relationships between brands/companies and their customers. In its design, the expectations and needs of consumers are absolutely central.
Customer Service focuses on the event when a customer asks for help and support and thus either contacts a support agent directly, or makes use of other support options offered (such as chatbot, ticketing system, etc.).

Customer Experience vs. User Experience (UX)
As digitization continues, the term user experience (UX) is increasingly used to describe a user’s experience with a digital product such as a website or software. More broadly, user experience describes the experience users have with a product, system, service, etc., while customer experience is the experience these users have with a brand in its entirety.
Thus, similar to the previously described customer service, user experience is one of many components and touchpoints of the overall customer experience.
Customer experience in online channels
In the digital era, interactions between companies and their customers have increasingly shifted to the Internet. Even companies that sell their products and services via brick-and-mortar stores now rely on an omnichannel strategy that integrates offline and online channels. Common omnichannel concepts have now evolved into what is known as unified commerce.
Unified commerce links all stationary and digital sales and communication channels on a common platform. It is designed to ensure that customers have seamless experiences at all relevant touchpoints, resulting in a uniform and consistently positive customer experience. An essential prerequisite for the realization of corresponding concepts and thus for the optimization of CX is that companies create a uniform data management system that is capable of capturing and integrating customer data from all channels.
What makes a good customer experience?
A positive customer experience occurs when all its aspects are seamlessly intertwined so that customers experience a brand and their interactions with it as positive and consistent. Key components in this context are:
Culture, processes and strategy
The development of CX is the responsibility of the company’s management. It is the duty of a company’s management to establish processes and strategies that guarantee a consistent customer experience throughout the entire customer journey, which also reflects the company’s culture.
High-quality products and services
The company’s offerings must meet consumer needs and expectations without compromise.
Reliable and transparent customer communication
A positive CX includes reliable and transparent customer communication. Relevant here are, in particular, marketing that generates realistic product expectations, high consulting and service quality, transparent pricing, but also reliable and quickly accessible support as well as proactive information in the event of problems.
People – employees and external partners
The development of a uniform CX involves the company’s own employees, but also external partners – including suppliers or service agents. They must understand the company’s strategy for shaping its customer relationships and be able to put it into practice. However, it is also important in this context that companies offer a compelling experience to their employees and other stakeholders who have an influence on CX. Corporate culture and brand identity are critical factors in both dimensions.
Information and technology
Integrated knowledge and data management is critical to success in optimizing CX. Companies must use digital technologies to create a modern CX environment for this purpose.
Why customer experience is important
In a 2019 study covering a total of 20 industries, consulting and research firm Qualtrics examined the impact of negative customer experiences on consumer behavior. Across industries, 45 percent of study participants had reduced or completely stopped spending after a bad experience with a company. The resulting loss of sales averaged three percent.
The high volatility of customer relationships must also be taken into account here – customers who are not satisfied with a company’s services can usually be sure of finding another provider that meets their needs after just a quick Google search.
The latest Zendesk Trends Report shows that around 50 percent of all customers switch to a competitor after just one bad experience, and over 80 percent decide to switch if they have more than one bad experience.
Positive customer experiences in all interactions and at all touchpoints, on the other hand, ensure high customer satisfaction. Companies benefit from high customer loyalty, positive feedback and referral marketing. At the same time, they optimize their opportunities to win new customers through positive CX.
What is Customer Experience Management (CEM / CXM)?
In order to maintain and further expand their competitive position, more and more companies are moving toward managing CX through targeted customer experience management (CXM, CEM). IT market research firm Gartner defines CXM as a practice that aims to design interactions with customers in a way that fully meets or exceeds their expectations.
The goal of CXM is to manage all customer experiences on a strategy-based basis and to optimize all touchpoints of the customer journey for this purpose. To do this, it must perform the following tasks:
- Measurement and analysis of the customer experience to identify optimization potentials
- Identification of customer needs and customer problems, for example through market research or customer surveys
- Planning, development and implementation of CX optimization measures
- Controlling, cost-benefit analyses
- Evaluation of measures and quality control of the service offering.
Through CXM, companies create the conditions for increasing the value of their brands and customer lifetime value (CLV). It strengthens brand loyalty and lowers costs by reducing customer churn.
Studies indicate that CX is the most important differentiator for brands today.
Source
Measuring Customer Experience – Goals and KPIs
Not all aspects of CX can be captured quantitatively and through key performance indicators, as the customer experience is also shaped by a wide range of subjective and emotional perceptions. Nevertheless, quantitative CX measurements are useful in some cases. They make it possible to gauge the current status of CX and make optimizations, gain insights about customers, and determine the effectiveness and return on investment (ROI) of optimization measures.
KPIs for measuring CX are the Net Promoter Score (NPS), the Customer Effort Score (CES) and the Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT), each of which is determined by customer surveys.
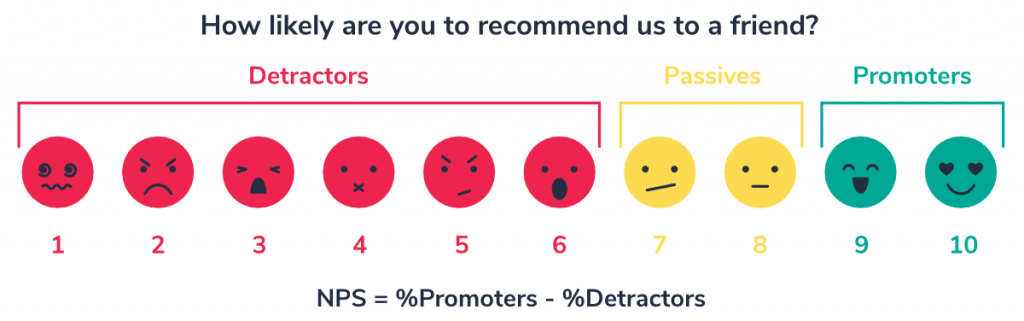
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The Net Promoter Score is an indicator of customer loyalty. The participants in the survey indicate on a ten-point scale the extent to which they are willing to recommend a brand in their private environment.
Depending on the rating given, they are divided into different groups – detractors (0-6), indifferents (7-8) and promoters (9-10 points) – and their percentage share of the total sample is calculated.
A high NPS indicates high customer loyalty, suggesting a positive customer experience.

Customer Effort Score (CES)
The Customer Effort Score indicates the effort required to clarify a matter with the company. For example, it can be asked how much effort a customer had to make to complete a purchase or reach the service hotline.
Five- or seven-point scales are used to determine the CES. The sum of the scores awarded is divided by the number of responses.
The higher the CES, the more time-consuming it is for the customer to contact the company.

Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
The Customer Satisfaction Score provides an indication of customer satisfaction. It does not refer to the entire customer journey – the overall satisfaction with a product or service in the post-purchase phase is measured.
Five-point scales are generally used to determine it. The CSAT is calculated by dividing the number of satisfied customers (scale response 4 or 5) by the number of all responses and multiplying the result by 100 – the percentage of satisfied customers is thus reported.
Tips for increasing the customer experience
You can improve the CX of your customers through various measures. Important in this context are, among others, continuous feedback from customers, employees and external partners, the establishment of an omnichannel strategy or unified commerce, support offers as part of your content management strategy, the creation of proactive customer experiences as well as active CXM and continuous data analyses.
Today, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also helping to optimize the customer experience. Common applications for this currently include mobile messaging and chatbots that take over routine tasks or decide to refer the customer to a human service agent.
AI can play a prominent role with regard to cross-channel, integrated data management.
Such an AI platform is capable of collecting and structuring all customer information and displaying the processed data for analysis purposes, e.g., in an individual dashboard.
Insaas.ai already supports some well-known B2B and B2C companies in this regard.
Companies thus gain insights that – unlike the common KPIs for measuring CX – also provide information about why their customers are satisfied or dissatisfied.
What drives the target customer group, what they think of products, product features and services, what they expect and what they need based on their preferences and challenges in the broader industry environment.
Customer insights analytics can help companies:
- improve customer retention in their business units
- make existing customer management more successful (up-/cross-selling)
- evaluate new business options (innovation, trend prediction)
- personalize the customer journey comprehensively and in a customer-oriented way


